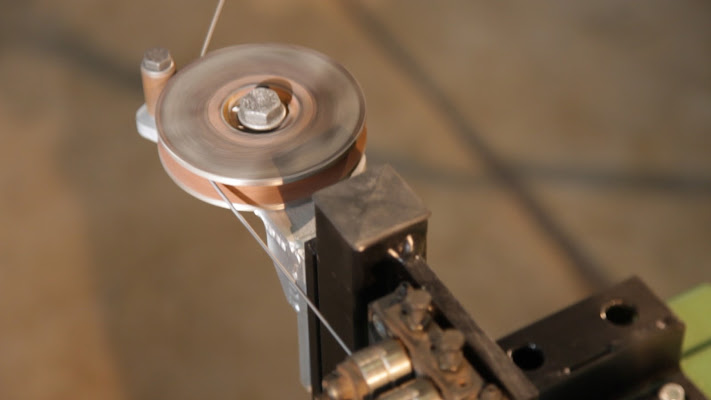
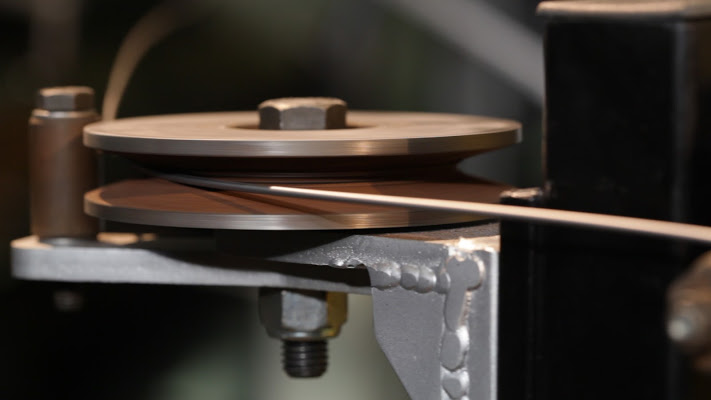
The third project, also started in autumn 2010 and concluded in autumn 2013 at the Trafileria and Zincheria Cavatorta factories, provided for the revision of much of the production cycle:
- a dry descaling phase of the wire rod, with the use of processing waste and recycling of the obtained wastes;
- a phase of cleaning and activation of the post-baking wire by means of microwave induced plasma treatment;
- a galvanizing phase in Zn-Al-Mg tertiary bath, able to operate at lower temperatures and with an increase in the quality of the finished product.
Documents
- Download the brochure of the project
- Download the article by Prof. Paolo Veronesi for the XIII International Conference on Microwave and RF Heating AMPERE 2011 – 5-6 Settembre 2011 – Toulouse, France”
- Download the Layman’s Report MDPATC
- Results achieved
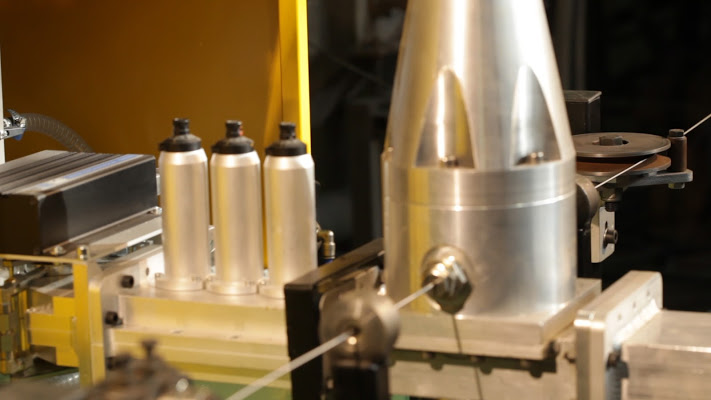
- Dip coating bath – functional details and photos
- Disseminative report
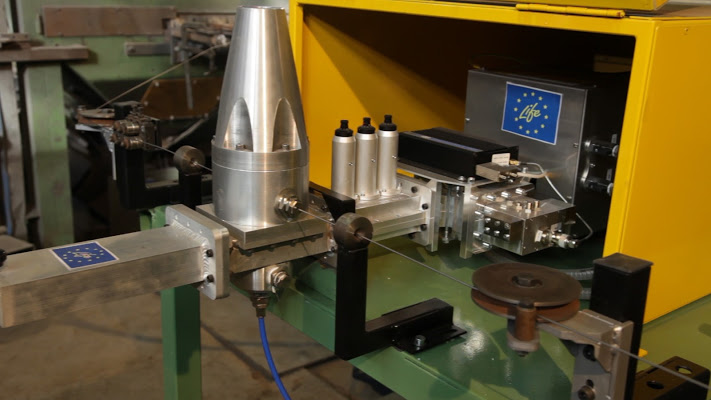
- Final Pilot line – functional details and photos
- Mass and Energy balance
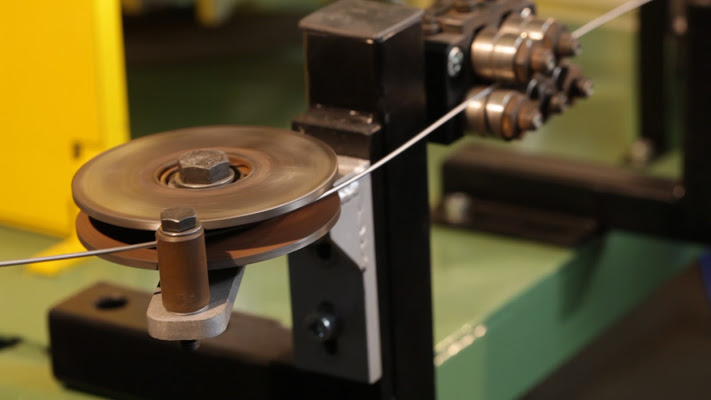
- Mechanical descaling system – functional details and photos
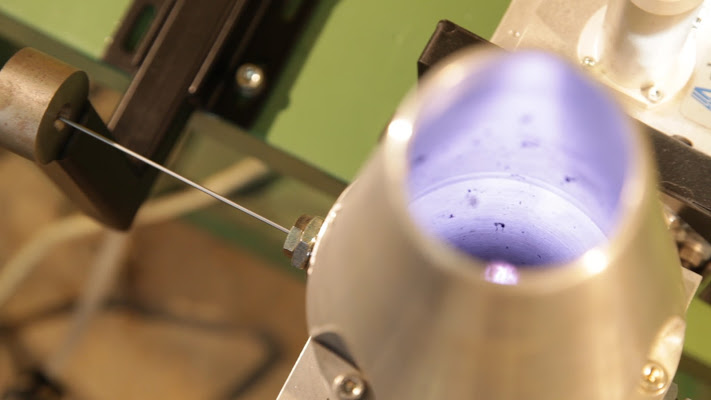
- Microwave and plasma applicator – functional details and photos
- Technical report MDPATC
LIFE+ PROGRAMME
The (EC) No 614/2007 Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23/05/2007 established the new European Programme for the financial support of products and technologies aimed at protecting the environment: LIFE +.
LIFE + replaces the previous LIFE program (Environment, Nature and Third Countries), the Community Framework Programme for cooperation in promoting sustainable urban development, the Community Action Programme for the promotion of non-governmental organizations active in the field of environmental protection and Forest Focus program.
The objective of LIFE is to contribute to the development, implementation and updating of policy and legislation on the environment. This financial instrument is also designed to facilitate the integration of environment into other policies and to contribute to sustainable development in the European Union.
LIFE + co-finances environmental activities in the European Union (EU) and in certain third countries (EU accession countries, members of the European Environment Agency, the Western Balkan countries affected by the process Stabilisation and Association). The funded projects may be proposed by operators, public and private bodies or institutions.
LIFE + consists of three thematic components:
- Nature and Biodiversity. The Nature projects contribute to the implementation and development of the guidelines “Birds”, “Habitat” and the Natura 2000 network. Biodiversity projects focus on innovative practices aimed at halting the loss of biodiversity in Europe.
- Environmental Policy and Governance. It supports innovative or demonstration projects that show innovative solutions relating to relevant environmental issues.
- Information and Communication. It supports projects aimed at the communication and awareness campaigns on the environment, and training initiatives and campaigns for the prevention of forest fires.
BACKGROUND & OBJECTIVES
Products derived from metal wire, such as nails, screws and wire mesh, are subjected to various chemical treatments, which improve performance, but have a strong impact on the environment.
In fact they involve:
- Very high energy consumption
- Consumption of water
- Use of hazardous chemicals
- Production of waste (sludge containing iron oxides, acids exhausted) to be disposed of
- Production of non-recyclable waste products
- Emissions into the atmosphere
The project aims to demonstrate the possibility of physical treatments in place of chemical ones, improving the environmental performance of the manufacturing process of products derived from wire and converting waste into re-usable products in any process.
PROJECT
Trafileria e Zincheria Cavatorta S.p.A, a company that has always paid attention to the implication arising from their work environment has decided to engage in an interesting and significant challenge: to prove that the treatment process of steel wire and nails can be done without the use of chemicals.
In particular treatment is used for dry cleaning of surface to be machined mechanically working through a process of descaling and grinding that does not require the use of sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid (highly toxic substances and pollutants) currently in use, then the phase drawing is performed by an innovative microwave plasma surface treatment in place of the traditional pre-treatment involving the use of ammonium chloride. To demonstrate the feasibility of the new process, the company intends to build a pilot plant capable of treating up to 1,000 kg / hour (4,000 tons / year) of wire rod. The project “MDPATC” was featured on LIFE + and subjected to the evaluation of the European Commission, which considered the project worthy of support for the aims and results for the innovation it offers.
DEVELOPMENT ACTIONS
To reach the realization of the pilot plant, the project has been studied and designed through the implementation of specific technical activities:
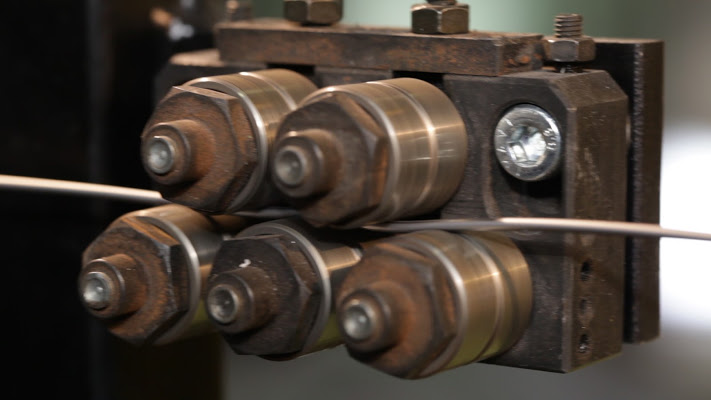
- mechanical descaling and grinding of the blade for the development of a system for the cleaning rod through the mechanical action of prismatic metal fragments, assisted by a system of magnetic separation of the abrasive particles are able to divide the particles of rounded shape from those still used as abrasive prismatic (characterization of waste arising from the manufacture of prismatic rods available, creation of test equipment for abrasive descaling of wire rod samples, characterization results and definition of project requirements for the descaling system, design and creation of a system of descaling of wire rod and grinding of the blades; design and construction of a mechanical and magnetic separation to produce iron oxide pigments and circular strokes for shot peening, the characterisation of the products obtained; evidence operating with continuous feed of wire rod);
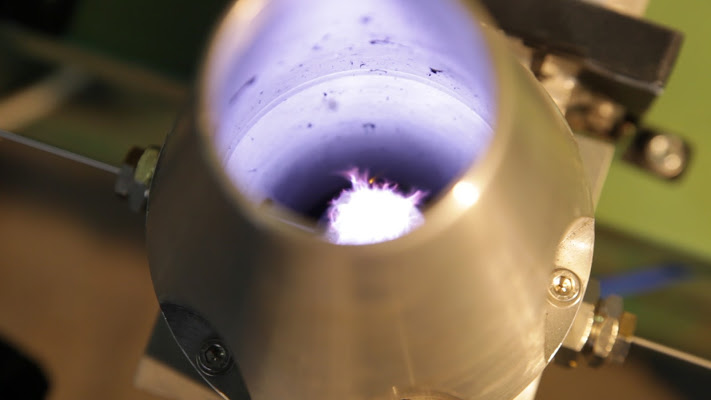
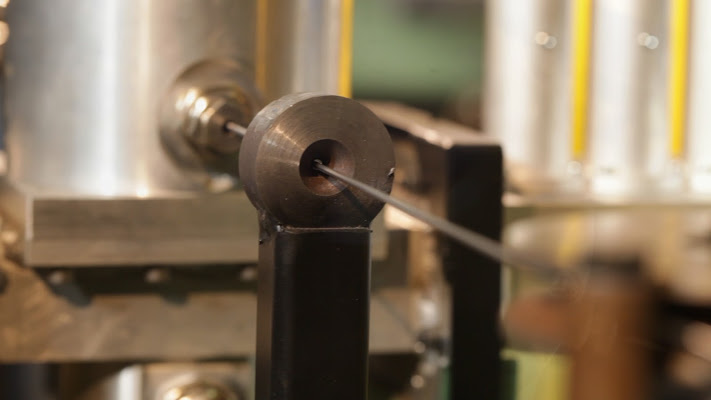
- microwave plasma treatment (definition of equivalent permittivity of the plasma based on its expected characteristics, numerical simulation and optimization of microwave applicators for plasma generation, numerical simulation of systems “suffocation” to prevent microwave leakage from the container microwave design and manufacture of microwave plasma sources, on the basis of numerical simulation results, including devices to prevent microwave leakage; tests on drawn wire and characterization of the results obtained, in terms of microstructure and homogeneity of treatment);
- dip-coating (design and optimization of the ternary mixture of alloy coating bath through the DOE system, design and construction of a bath of dip-coating and auxiliary components, design and construction of transportation systems for transit wire in the coating bath, hot bath running tests on the dip-coating, in the optimized conditions, and further optimization of process parameters, characterization results and mass balance and energy of the coating bath, including a quantification of emissions);
- assembly of the pilot line (design and optimization of the layout of the pilot line, pilot line installation and construction of transportation systems, connections, safety devices, cabling, connection to the auxiliary tests of continuous operation with different rods and varying treatment parameters, characterization of the products obtained, especially in terms of corrosion resistance and weld microstructures, mass balance, energy and environmental assessment of actual achievements and results obtained).
Technical activities were thought to be carried out simultaneously with other activities necessary for the realization of the project and in particular:
- management activities of the entire project, both administratively and technically-organizational;
- monitoring activities to be aware of the situation in real time progress of the project and the results compared to those initially set;
- dissemination of results of activities with the intent to make available to interested project progress and results achieved gradually;
- realization of an after-LIFE Communication Plan, in order to plan a more effective and lasting dissemination of project results also after ended.
EXPECTED RESULTS
The current production cycle of the rod has a high environmental impact:
- Not directly recyclable waste production (zinc coating prevents the direct recast)
- Production of greenhouse gases and liquid acids (from pickling and descaling chemical)
- Production of spent acid for disposal (only a fraction of which can be re-generated)
- Production of sludge for disposal (which also contain iron oxides)
- Use of large amounts of water
- Use of thick coatings of zinc to meet the interface reactions and the fragility of the compounds
- Use of energy (for heating baths for pickling and for maintaining a bath of molten zinc)
- Use of flow agents and surface active compounds such as ammonium chloride, to improve adhesion of the zinc coating
The proposed project, however, has been designed to realize a more “green” process able to:
- value 2,000 tons of waste metal to be used in the process of mechanical descaling, peening and converting them into particles of iron oxide pigments;
- reduce the consumption of electricity in descaling and coating hot-dip of 480,000 kWh per year (120 kWh per tonne);
- obtain a water savings of 25,000 m3 per year;
- reduce the production of acid sludge of 2,500 tonnes per year;
- save the use of 6,000 tons of hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid compared to the processes that are still using acid descaling and pickling;
- reduce emissions of toxic fumes from hot dip coating baths depending on the composition of the bath;
- reduce the production of zinc ash due to better protection against oxidation of the bath dip coating.
PROJECT DEVELOPMENT
The project regularly started in November 2010.
Management and monitoring actions were planned and are giving excellent results and allow the project to run smoothly, as according to the expected times, objectives and costs. From a technical point of view, the project started with the experimental phase of mechanical descaling, with the fitting of a special cleaning system of the rod through the combined use of grit and production residues.
The descaling machine has three turbines set at angles of 120° as regards to the wire rod, so as to permit optimum cleaning of the product in transit. Through a cyclone and sieve combined separation system it is possible to separate the iron oxide that got detached from the surface of the wire rod, the still reusable abrasive material and the abrasive material that is no longer suitable for processing.
Meanwhile, with the collaboration of the Department of Materials Engineering and the Environment, of the Modena and Reggio Emilia University, the work relating to the plasma processing induced by microwave started. The numerical simulation phase was achieved, supported by a first experimental phase carried out in the laboratories of the University, and then a second experimental phase on a laboratory prototype with the use of wire samples of a different nature and diameter made by Trafileria e Zincheria Cavatorta.
After which further in-house tests were carried out, with a higher powered and water-cooling plasma system, which demonstrated the feasibility of the surface treatment. The various tests carried out led us to seek different solutions (with cones welded to the waveguide, with the first cone integrated into the second one or with collapsible cones, and again with different cooling and inlet gas preheating systems) which enabled the plasma torch to be designed and created in the final version, i.e. able to considerably improve the homogeneity and complete treatment of the wire, a feature that has required some additional work.
Regarding the recoating of the wire with metal alloy, tests were initially carried out for recoating with Zn-Al alloy on product samples made with the experimental stages. The results obtained were very encouraging, as the alloy coating showed an improvement of corrosion resistance and superior mechanical characteristics compared to a coating of pure zinc.
The next step was to introduce small percentages of Mg into the alloy as well, thu8s it was possible to obtain the most suitable gas mixtures and we are finishing the final testing work of the wire coating with this mixture. There are also on-going tests to determine the more efficient operating temperature and consequently the residence time of the wire in the tank which ensures a cost/result efficiency.
The addition of rare earths up to now has proved superfluous, since the expected results were obtained only with the application of the determined Zn-Al-Mg mixture. We will try further additions of earths with the final tests on the final pilot plant, which has been sized and whose many components are already available.
From the mechanical point of view, the cover of the tank has been prepared for the Zn-Al-Mg baths to contain the reaction mixture in an appropriate manner and ensure more purity to the wire and a better, less contaminated application. The entry and exit stations of the wire from the system have also been prepared, by means of unwinding and winding.
Regarding the implementation of the demonstrative pilot line, which will have a production capacity of about 1000 kg per hour of iron products in the form of drawn wires, much work has, in fact, already been done. All of the components of the pilot line have already been made, and a semi-continuous production line has already been tested to test the effects of the process variables, in particular of the plasma treatment, on the properties of the materials. Once the final configuration of the wire coating phase is completed, the application of the plasma will be continued with the immersion and the pilot line will thus be completed and the last tests on the coating alloy will be carried out, in order to lead to the best resistance to corrosion with the minimum immersion temperature.
The dissemination phase of the project was also started, with the creation of this website, and being restyled, and notice boards, placed in the company and at the head office of the Cavatorta group. A first presentation of the project was made at the trade fair in Helsinki in October 2011 and then at Big 5 Show trade fair in Dubai.
The first results of the project were presented by Prof. Veronesi of the Department of Engineering, of the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia to AMPERE, 2011, an international conference on microwaves, held in Toulouse in September 2011. The presentation has become an article, published in the book “Microwave and RF power applications”.
A brief summary of the project, its objectives and initial results have also become a technical article published in the magazine “Technologies of Wire” on “Edilportale” and news dedicated to the general public, published in December 2011 on the Official Parma Gazzetta di Parma.
In June, 2012, for the twentieth anniversary of the LIFE instrument, an event was organized at the venue of Metallurgica Abruzzese SpA, which included the participation of public authorities, representatives of trade associations, companies of this sector and of others, as well as consultants and former officials of the European Commission, during which there was a presentation of the LIFE programme, its history, principles that inspired it and the 2012 tender, as well as the projects in progress of the Cavatorta group (including MDPATC).
(Update: May 2013)
EVENTS
A final event has been organized on 28 March 2014, after the conclusion of the project. During the event information on the results achieved in economic and environmental terms have been disclosed and product samples have been given to those interested. The turnout was fairly good and mainly involved representatives of the industry and universities as well as representatives of the public administration. During the final event the cooperation of those present for networking and transfer of technology was publicly requested; some companies have shown interest in this activity for future development of the results of the project. Following, the program, the main presentation used and some photos of the event.